It is reported that Samsung, Micron, and Hynix, the three major international DRAM giants, plan to reduce DDR4 production. Research firm TrendForce expects that the last supply of DDR4 memory from each supplier will be around early 2026. Samsung was the first to announce that it will end the life cycle of its DDR4 product line at the end of 2025, with the final order date scheduled for early June. Micron also officially notified its core customers, confirming that DDR4/LPDDR4 products will be gradually discontinued in the next 2 to 3 quarters.
In line with the trend of production cuts and supply suspensions, DDR4 market prices have risen sharply. Micron's official pricing for DDR4 in June rose by 50%, and the price of 16Gb in the spot market also soared to US$6, even exceeding the same specification of DDR5. Market data shows that Samsung's DDR4 8Gb spot price has soared to about US$4.8, significantly higher than the recent average price of US$3.3, and the market price is in a state of chaos.
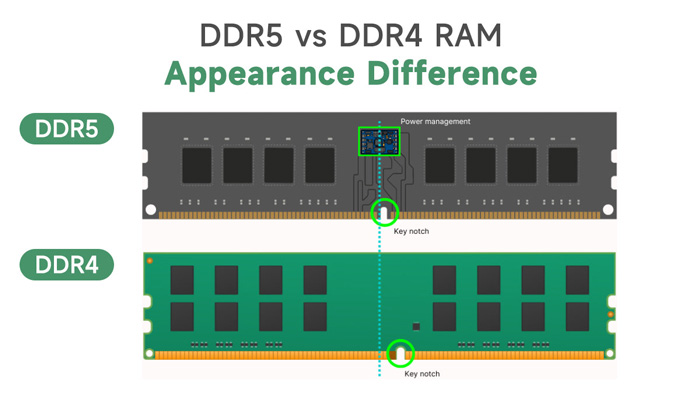
DDR4 vs DDR5: Technology Iteration Accelerates DDR5 to Replace DDR4
DDR4 memory is the fourth generation of double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory. It is the core hardware used in computers and electronic devices to temporarily store running data. As the mainstream memory standard from 2014 to 2024, DDR4 memory has promoted the performance leap of PCs, servers, and smart devices. Its core value lies in balancing speed, power consumption, and cost.
Source from Internet
DDR5 is a disruptive upgrade of DDR4. The bandwidth is directly doubled (starting at 4800MHz vs 3200MHz of DDR4). Through the dual-channel design (independent 32-bit channel per module), it achieves a leap in concurrent data throughput, which can meet high-load requirements such as AI computing and 8K video processing; at the same time, the voltage is reduced to 1.1V, the power consumption is reduced by 20%, and the on-chip ECC error correction mechanism significantly improves the energy efficiency ratio and data reliability. However, DDR4 is limited to a single-channel 64-bit architecture, and its performance cannot be further improved. It only relies on mature ecology and low price advantages (30%-50% lower price for the same capacity) to support the transition of the old platform.
The complete discontinuation of DDR4 memory will not only directly impact the price system and supply chain, but will also accelerate the reshuffling of the industry structure and technology iteration. Although DDR5 has replaced DDR4, most devices on the market still run DDR4, which cannot be eliminated in the short term and will still exist in the industrial and maintenance markets in the future.
Factors Driving Industrial Transformation
The sudden drop in supply has caused some traders to raise prices, especially for high-specification DDR4. However, there is a lag in the switch of terminals to DDR5, and low-end and mid-end devices (such as industrial computers and old PCs) face a sharp increase in costs due to their reliance on DDR4.
The main reasons for accelerating the elimination of DDR4 include:
1. Production capacity tilts toward high-value-added products
To meet the explosive demand for AI servers, high-performance computing, and next-generation mobile devices, wafer production capacity must be allocated first to high-value-added storage products such as DDR5, LPDDR5/X, and HBM, which are more technologically advanced and profitable, and whose profit margins can reach more than three times that of DDR4.
2. Pressure to optimize profit structure
The profit margin of DDR4 products in the consumer electronics field has been severely compressed, far lower than high-profit markets such as enterprise-level storage, automotive chips, and HBM (high-bandwidth memory). Reducing DDR4 production is an inevitable choice for factories to focus on high-return businesses. The gross profit margin of consumer-grade DDR4 is less than 5%, while HBM exceeds 60%.
3. Mature technology generation switching
DDR5 has completed market verification with its advantages of doubling bandwidth, improving energy efficiency, and capacity density. Combined with the full support of Intel and AMD's new platforms, its ecosystem is ready to fully replace DDR4.
Conclusion
In the short term, DDR4 supply shortages and sharp price fluctuations are inevitable. Downstream system manufacturers and module companies will face the dual pressures of tight supply chains and surging costs. The violent fluctuations in the spot market are expected to continue until the original factory capacity conversion is completed in mid-2026. In the long run, this round of production cuts marks the full arrival of the DDR5 era. In the next 12-18 months, DDR5 will become the absolute mainstream in servers, high-end PCs, and new smartphones. At the same time, the strategic competition among the three major original factories for HBM, LPDDR5X, and advanced packaging technology will enter a white-hot stage.