You may find capacitors in almost all circuit boards. The popular types include ceramic capacitors and electrolytic capacitors. For decades, engineers have faced a fundamental choice in circuit design: ceramic or electrolytic capacitors? With rapid advancements in materials science and electronics miniaturization, the answer is more nuanced than ever. Both have evolved dramatically, but their core differences remain pivotal to smart component selection. Let’s cut through the hype.
What are Capacitors?
You can imagine them as tiny electronic reservoirs that store and release electrical energy. The capacitors consist of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric, an insulating material.
They accumulate an electric charge when voltage is applied across the plates. Then release when the voltage is removed or the circuit requires a burst of energy.
Capacitance measures the energy stored in the electric field generated between two points when there is a given potential difference. It is often called the "dual" of inductance. Just as inductance refers to the energy stored in a magnetic field for a given current, capacitance does the same, except the energy stored in the electric field is stored via the potential difference rather than the current.
Capacitors store energy in the dielectric rather than in the plates. Their effectiveness is determined by the physical size and the dielectric constant of the insulating layer between the plates. Physical size refers to the area of the plates and the distance between them. The larger the area, the greater the electric field; the closer the plates are, the stronger the field. (Field strength is measured in volts per meter; the same potential difference produces a stronger field over a shorter distance.)
The dielectric constant is how strong a field will be generated in a specific medium. The 'baseline' dielectric constant is ε, with a normalized value of 1. This is the dielectric constant of a perfect vacuum, or the field strength that occurs through spacetime.
Now we learn about what capacitors are, let’s find out the two most popular types: electrolytic and ceramic capacitors.
Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors typically have very high capacitance values. They can store large amounts of electrical energy, even tens to hundreds of times larger than other types of capacitors. So they generally used in high-stability oscillation circuits, mainly as loop and pad capacitors.

Their capacitance tend to have a large range, going from microfarads (µF) to farads (F), which are on the larger end of capacitance spectrum.
This type of capacitors have a cylindrical shape resembling a tube. They use metal foil and electrolyte to build the plates, with an oxide film for insulation. This structure gives them high volumetric energy density. You can see that there are two polarity, one side is shorter than the other, something unique to electrolytic capacitors. If reversed or mixed up, the capacitors may fail to work or even explode.
The metal foil of the electrolytic capacitor is the positive electrode (aluminum or tantalum), and the oxide film (aluminum oxide or tantalum pentoxide) close to the positive electrode serves as the dielectric. The cathode is composed of a conductive material, an electrolyte (the electrolyte can be liquid or solid), and other materials.
Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors use a ceramic as their dielectric, with metallization on either side as the plates. Because MLCC (Multi-layer Ceramic Capacitors) are stacked in a staggered manner, they are much smaller than other capacitors. So they are more suitable for portable devices, which require compact components.

Their capacitance is generally small and is usually used in bypass (decoupling), coupling, filtering, resonance, temperature compensation, tuning, energy storage, etc. Due to its advantages of high reliability, small size, low loss, and easy mounting, it has quickly become the preferred type of capacitor in the electronics industry.
Difference Between Electrolytic and Ceramic Capacitors
At their most basic, ceramic and electrolytic capacitors are separated by how they store energy. The capacitance of ceramic capacitors is lower than that of electrolytic.
Ceramic capacitors can achieve more than 100μF in 1210 packages but suffer voltage derating—Y5V types lose ~70% capacitance at 50% rated voltage. Solid-state electrolytics dominate new designs. Polymer electrolytes slash ESR, boost ripple current handling, and last 3 times longer than wet types.
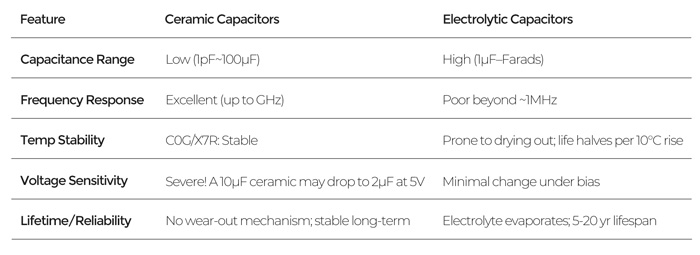
Electrolytic vs Ceramic Capacitors
When choosing between ceramic and electrolytic capacitors, consider the application and circuit characteristics. If the circuit requires high-frequency and high-voltage operation, select an electrolytic capacitor. If the circuit needs to operate for extended periods or requires high energy storage capacity, a ceramic capacitor may be better. It depends on the specific application.
Advantage of Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors have a high dielectric constant and good stability, allowing them to operate at higher temperatures. Furthermore, their compact and lightweight design makes them easy to carry and install. They are suitable for high-frequency and high-voltage circuits because the near-zero ESL/ESR suppresses noise up to GHz ranges.
It is ideal for space-constrained applications, such as wearables/IoT and smartphones. However, ceramic capacitors have limited energy storage capacity and a relatively short lifespan, requiring frequent replacement.
Advantage of Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors have the ability to store and release electrical charge, allowing them to store large amounts of charge, making them suitable for low-frequency and low-voltage circuits. In contrast to ceramic capacitors, they have a relatively long service life and do not require frequent replacement.
With power supply bulk filtering, they deliver affordable high-C (from 100μF to 10mF). Electric vehicles use them for regenerative braking due to high energy density.
However, electrolytic capacitors have limited energy storage capacity, perform poorly in high-frequency and high-voltage environments, and are bulky and heavy.
Can Ceramic Capacitors Replace Electrolytic Capacitors?
Comparing the two types of capacitors, ceramic capacitors have better frequency characteristics than electrolytic capacitors. If you're replacing a ceramic capacitor, consider the frequency band you're using. It's possible to replace it even if the capacitance is different from that of an electrolytic capacitor. Ceramic capacitors have very low ESR, so replacing them may cause abnormal oscillation, but this can be suppressed by adjusting the constants in the phase compensation circuit.
When replacing an electrolytic capacitor, you can select an equivalent product based on parameters, such as series, capacitance, and voltage. Alternatively, after confirming the impedance within the frequency band, you can enter the required criteria in the advanced search of Murata's design support software, SimSurfing, and select a model that meets these requirements.